GST is a huge reform for indirect taxation in India, the likes of which the country has not seen post Independence. GST will simplify indirect taxation, reduce complexities, and remove the cascading effect. It will have a huge impact on businesses, both big and small, and change the way the economy functions.
GST Overview, Goods and Service Tax Overview With Example
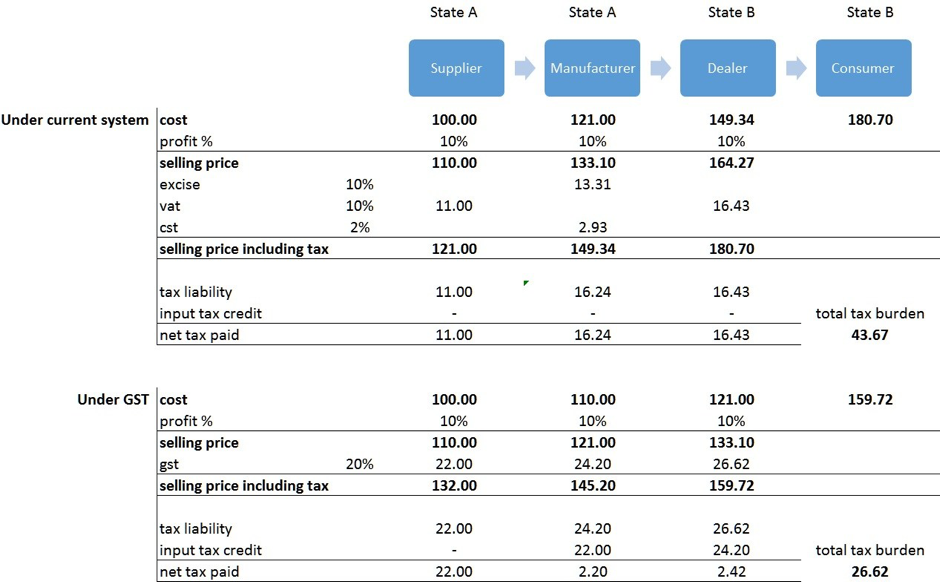
- GST is a single tax on the supply of goods and services, right from the manufacturer to the consumer.
- Credits of input taxes paid at each stage will be available in the subsequent stage of value addition, which makes GST essentially a tax only on value addition at each stage.
- The final consumer will thus bear only the GST charged by the last dealer in the Supply chain with setoff benefits at all the previous stages.
- At the Central level, the following taxes are being subsumed:
Central Excise Duty,Additional Excise Duty,Service Tax,Additional Customs Duty commonly known as Countervailing Duty, andSpecial Additional Duty of Customs.
5) At the State level, the following taxes are being subsumed:
Subsuming of State Value Added Tax/Sales Tax,Entertainment Tax (other than the tax levied by the local bodies), CSTOctroi and Entry tax,Purchase Tax,Luxury tax, andTaxes on lottery, betting and gambling.
- : The Central GST and the State GST would be levied simultaneously on every transaction of supply of goods and services except on exempted goods and services, goods which are outside the purview of GST and the transactions which are below the prescribed threshold limits. Further, both would be levied on the same price or value unlike State VAT which is levied on the value of the goods inclusive of Central Excise.
- Cross utilization of credit of CGST between goods and services would be allowed. Similarly, the facility of cross utilization of credit will be available in case of SGST. However, the cross utilization of CGST and SGST would not be allowed except in the case of interstate supply of goods and services under the IGST model
- In case of interstate transactions, the Centre would levy and collect the Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) on all interstate supplies of goods and services under Article 269A (1) of the Constitution. The IGST would roughly be equal to CGST plus SGST. The IGST mechanism has been designed to ensure seamless flow of input tax credit from one State to another. The interstate seller would pay IGST on the sale of his goods to the Central Government after adjusting credit of IGST, CGST and SGST on his purchases (in that order). The exporting State will transfer to the Centre the credit of SGST used in payment of IGST. The importing dealer will claim credit of IGST while discharging his output tax liability (both CGST and SGST) in his own State. The Centre will transfer to the importing State the credit of IGST used in payment of SGST. Since GST is a destination based tax, all SGST on the final product will ordinarily accrue to the consuming State.
- The major features of the proposed payments procedures under GST are as follows:
- The States are also of the view that Composition/Compounding Scheme for the purpose of GST should have an upper ceiling on gross annual turnover and a floor tax rate with respect to gross annual turnover. In particular, there would be a compounding cut-off at Rs. 50 lakh of gross annual turnover and a floor rate of 0.5% across the States. The scheme would also allow option for GST registration for dealers with turnover below the compounding cut-off.
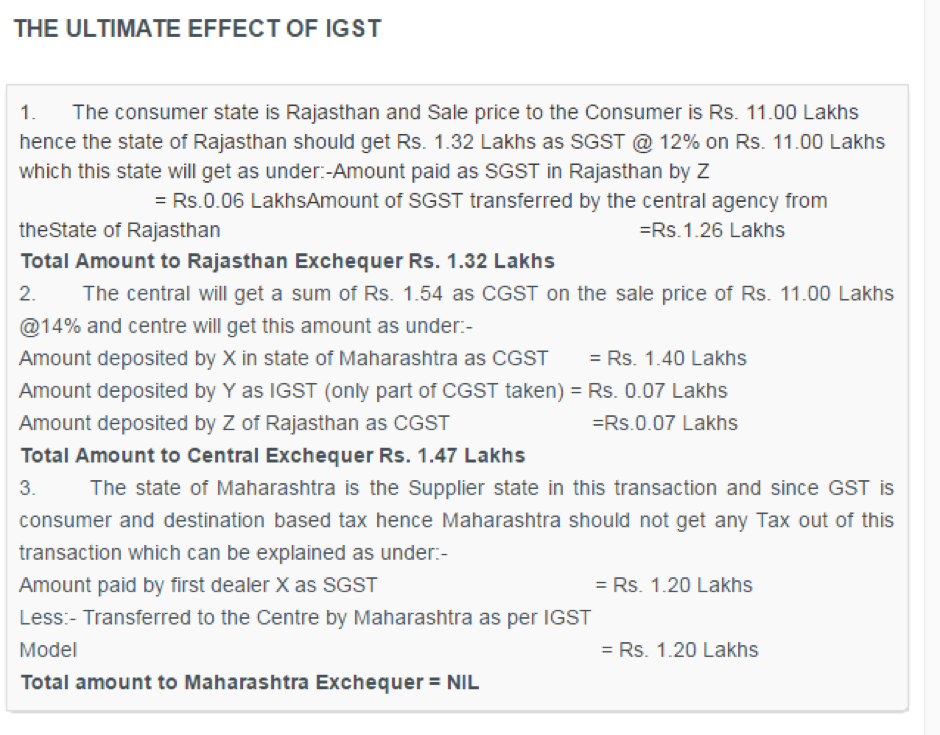
- Each taxpayer would be allotted a PAN-linked taxpayer identification number with a total of 13/15 digits. This would bring the GST PAN-linked system in line with the prevailing PAN-based system for Income tax, facilitating data exchange and taxpayer compliance. EXAMPLE:- X of Mumbai sold Goods worth Rs. 10.00 Lakhs to Y of Mumbai and Y of Mumbai sold the same goods to Z of Rajasthan at Rs. 10.50 Lakhs.Now at second stage Z of Rajasthan sold the same goods to a consumer in Rajasthan at Rs.11.00 Lakhs.Suppose the rate of SGST is 12% and rate of CGST is 14%. That will complete the full circle of IGST. THE ULTIMATE EFFECT OF IGST Recommended Articles